rcsofttech/audit-trail-bundle
最新稳定版本:v1.7.4
Composer 安装命令:
composer require rcsofttech/audit-trail-bundle
包简介
Enterprise-grade, high-performance Symfony audit trail bundle. Automatically track Doctrine entity changes with split-phase architecture, multiple transports (HTTP, Queue, Doctrine), and sensitive data masking.
关键字:
README 文档
README
Enterprise-grade, high-performance audit trail solution for Symfony.
AuditTrailBundle is a modern, lightweight bundle that automatically tracks and stores Doctrine ORM entity changes. Built for performance and compliance, it uses a unique Split-Phase Architecture to ensure your application stays fast even under heavy load.
Key Features
- High Performance: Non-blocking audits using a Split-Phase Architecture (capture in
onFlush, dispatch inpostFlush). - Multiple Transports:
- Doctrine: Store logs in your local database (default).
- HTTP: Stream logs to external APIs (ELK, Splunk, etc.).
- Queue: Offload processing to Symfony Messenger (RabbitMQ, Redis).
- Deep Collection Tracking: Tracks Many-to-Many and One-to-Many changes with precision (logs exact IDs).
- Sensitive Data Masking: Native support for
#[SensitiveParameter]and custom#[Sensitive]attributes for GDPR compliance. - Safe Revert Support: Easily roll back entities to any point in history, including associations.
- Conditional Auditing: Skip logs based on runtime conditions using Symfony ExpressionLanguage or custom voters.
- Rich Context Tracking: Automatically track Impersonation and store arbitrary metadata in a JSON
contextcolumn. - Modern Stack: Built for PHP 8.4+, Symfony 7.4+, and Doctrine ORM 3.0+.
Why AuditTrailBundle?
Most Symfony audit solutions either:
- Slow down Doctrine flush operations
- Log incomplete transactional data
- Cannot safely revert changes
- Are hard to extend beyond database storage
AuditTrailBundle is designed for production-grade auditing with:
- Minimal write overhead: Split-phase architecture ensures your app stays fast.
- Transaction-aware logging: Group related changes under a single transaction hash.
- Safe revert support: Easily roll back entities to any point in history, including associations.
- Multiple transport strategies: Store logs in DB, send to an API, or offload to a Queue (Messenger).
Architecture
This bundle is built using a Split-Phase Audit Architecture to ensure high performance and reliability in Symfony applications.
- Phase 1 (Capture): Listens to Doctrine
onFlushto capture changes without slowing down the transaction. - Phase 2 (Dispatch): Dispatches audits in
postFlushvia your chosen transport.
For a deep dive into the design decisions and how the split-phase approach works, check out the full article on Medium: Designing a Split-Phase Audit Architecture for Symfony
Quick Start
1. Installation
composer require rcsofttech/audit-trail-bundle
2. Database Setup (Doctrine Transport)
If you are using the Doctrine Transport (default), update your database schema:
php bin/console make:migration php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate
3. Basic Usage
Add the #[Auditable] attribute to any Doctrine entity you want to track.
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Attribute\Auditable; #[ORM\Entity] #[Auditable(ignoredProperties: ['internalCode'])] class Product { #[ORM\Id, ORM\GeneratedValue, ORM\Column] private ?int $id = null; #[ORM\Column] private string $name; #[ORM\Column] private ?string $internalCode = null; }
Configuration
Create a configuration file at config/packages/audit_trail.yaml.
For detailed transport configuration and usage, see
audit-transports.
audit_trail: # Enable or disable the bundle globally enabled: true # Global list of properties to ignore (e.g., timestamps) ignored_properties: ['updatedAt', 'updated_at', 'password', 'token'] # Global list of entities to ignore ignored_entities: [] # Retention period for database logs (in days) retention_days: 365 # Context tracking track_ip_address: true track_user_agent: true # enable or disable delete tracking enable_hard_delete: true enable_soft_delete: true soft_delete_field: 'deletedAt' transports: # Store logs in the local database doctrine: true # Send logs to an external API http: enabled: false endpoint: 'https://audit-service.internal/api/logs' # Dispatch logs to a message queue queue: enabled: false bus: 'messenger.bus.default' # Optional: specify a custom bus # Integrity & Signing # ------------------- # Enable cryptographic signing of audit logs to prevent tampering. integrity: enabled: true secret: '%env(AUDIT_INTEGRITY_SECRET)%' algorithm: 'sha256' # Transaction Safety & Performance # -------------------------------- # true (Default): Audits are sent AFTER the transaction commits (postFlush). # - Pros: High performance, non-blocking. Main transaction succeeds even if audit fails. # - Cons: Small risk of "data without audit" if app crashes between commit and audit. # - Recommended for: External transports (HTTP, Queue). # # false: Audits are sent DURING the transaction (onFlush). # - Pros: Strict atomicity. Data and audit are committed together. # - Cons: Slower. If audit transport fails, the entire transaction rolls back. # - Recommended for: Doctrine transport (when strict compliance is required). defer_transport_until_commit: true # If true, an exception in the transport will stop execution (and rollback if defer=false). # If false (default), transport errors are logged but execution continues. fail_on_transport_error: false
Detailed Usage
1. Granular Control
You can ignore specific properties or enable/disable auditing per entity via the class-level attribute.
#[Auditable(enabled: true, ignoredProperties: ['internalCode'])] class Product { private ?string $internalCode = null; }
2. Masking Sensitive Fields
Sensitive data is automatically masked in audit logs.
Option 1: Use PHP's #[SensitiveParameter]
public function __construct( #[\SensitiveParameter] private string $password, ) {}
Option 2: Use #[Sensitive]
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Attribute\Sensitive; #[Sensitive(mask: '****')] private string $ssn;
3. Conditional Auditing
Skip auditing based on runtime conditions using the #[AuditCondition] attribute or custom voters.
Option 1: Using ExpressionLanguage
Add the #[AuditCondition] attribute to your entity. You have access to object, action, changeSet, and user.
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Attribute\AuditCondition; use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Attribute\Auditable; #[Auditable] #[AuditCondition("action == 'update' and object.getPrice() > 100")] class Product { public function getPrice(): int { ... } }
Available Context Variables:
object: The entity being audited.action: The action being performed (create,update,delete, etc.).changeSet: The array of changes.user: An object containingid,username, andip.
Option 2: Custom Voters
For complex logic, implement the AuditVoterInterface. Your voter will be automatically discovered if it's registered as a service.
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Contract\AuditVoterInterface; class MyCustomVoter implements AuditVoterInterface { public function vote(object $entity, string $action, array $changeSet): bool { // Return false to skip auditing return $action !== 'delete' || $this->isAdmin(); } }
4. Rich Context & Impersonation Tracking
The bundle automatically tracks rich context for every audit log, stored in a flexible JSON context column.
Impersonation Tracking
If an admin is impersonating a user (using Symfony's _switch_user), the bundle automatically records the impersonator's ID and username in the audit log context.
$entry = $auditReader->forEntity(Product::class, '123')->getFirstResult(); $context = $entry->getContext(); if (isset($context['impersonation'])) { echo "Action performed by " . $context['impersonation']['impersonator_username']; }
Custom Context
You can manually add custom metadata to your audit logs by implementing the AuditContextContributorInterface. This is the recommended way to add application-specific information like correlation IDs, app versions, or feature flags.
namespace App\Audit; use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Contract\AuditContextContributorInterface; class SystemInfoContributor implements AuditContextContributorInterface { public function contribute(object $entity, string $action, array $changeSet): array { return [ 'app_version' => 'v2.4.1', 'server_node' => gethostname(), ]; } }
The bundle automatically discovers and executes all tagged contributors, merging their results into the context JSON column.
5. Events & Customization
The bundle dispatches Symfony events that allow you to hook into the audit process.
AuditLogCreatedEvent
Dispatched immediately after an AuditLog object is created but before it is persisted or sent to a transport. Use this to:
- Add custom metadata to the
context. - Modify the audit log data.
- Trigger external notifications.
namespace App\EventSubscriber; use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Event\AuditLogCreatedEvent; use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventSubscriberInterface; class AuditSubscriber implements EventSubscriberInterface { public static function getSubscribedEvents(): array { return [ AuditLogCreatedEvent::NAME => 'onAuditLogCreated', ]; } public function onAuditLogCreated(AuditLogCreatedEvent $event): void { $log = $event->getAuditLog(); // Add custom metadata $context = $log->getContext(); $context['server_id'] = 'node-01'; } }
AuditMessageStampEvent
Dispatched when an audit message is about to be sent via the Messenger transport. Use this to add custom stamps (e.g., DelayStamp, AmqpStamp) to the message.
namespace App\EventSubscriber; use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Event\AuditMessageStampEvent; use Symfony\Component\EventDispatcher\EventSubscriberInterface; use Symfony\Component\Messenger\Stamp\DelayStamp; class AuditStampSubscriber implements EventSubscriberInterface { public static function getSubscribedEvents(): array { return [ AuditMessageStampEvent::class => 'onAuditMessageStamp', ]; } public function onAuditMessageStamp(AuditMessageStampEvent $event): void { // Add a 5-second delay to all audit messages $event->addStamp(new DelayStamp(5000)); } }
6. Programmatic Audit Retrieval (Reader / Query API)
Read and query audit logs programmatically using a dedicated, read-only API.
→ Audit Reader Documentation (Symfony & Doctrine)
CLI Commands
The bundle provides several commands for managing audit logs.
List Audit Logs
php bin/console audit:list --entity=User --action=update --limit=50
Purge Old Logs
php bin/console audit:purge --before="30 days ago" --force
Export Logs
php bin/console audit:export --format=json --output=audits.json
View Diff
php bin/console audit:diff User 42
Revert Entity Changes
AuditTrailBundle provides a powerful Point-in-Time Restore capability, allowing you to undo accidental changes or recover data from any point in your audit history.
# Revert an entity to its state in a specific audit log php bin/console audit:revert 123 # Revert with custom context (JSON) php bin/console audit:revert 123 --context='{"reason": "Accidental deletion", "ticket": "T-101"}'
Custom Context on Revert
You can pass custom context when programmatically reverting an entity. This is useful for tracking why a revert was performed.
$auditReverter->revert($log, false, false, [ 'reason' => 'Accidental deletion', 'ticket_id' => 'TICKET-456' ]);
The bundle also automatically adds reverted_log_id to the context of the new audit log, linking it back to the original entry.
Why it's "Safe":
- Association Awareness: Automatically handles entity relations and collections.
- Soft-Delete Support: Temporarily restores soft-deleted entities to apply the revert.
- Dry Run Mode: Preview exactly what will change before applying (
--dry-run). - Data Integrity: Ensures the entity remains in a valid state after the rollback.
Tip
Use the revert feature for emergency data recovery, undoing unauthorized changes, or restoring accidental deletions with full confidence.
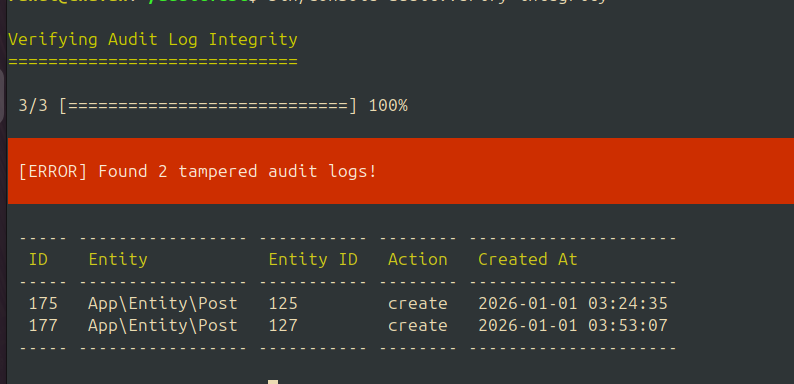
Verify Audit Log Integrity
Ensure the integrity of your audit logs by detecting any unauthorized tampering or modifications. This command validates cryptographic hashes to identify compromised records.
php bin/console audit:verify-integrity
Use Cases:
- Compliance Audits: Verify that audit logs haven't been altered for regulatory compliance (SOX, HIPAA, GDPR).
- Security Monitoring: Detect unauthorized tampering after security incidents.
- Historical Data Verification: Confirm past records are accurate and trustworthy.
Example Output:
Warning
Any tampered logs indicate a serious security breach. Investigate immediately and review access controls to your database.
Any tampered logs indicate a serious security breach. Investigate immediately and review access controls to your database.
Transport Payload Signing
When using HTTP or Queue transports with integrity enabled, the bundle automatically signs the payload to ensure data authenticity during transit.
HTTP Transport
The bundle adds an X-Signature header to the HTTP request containing the HMAC signature of the JSON body.
POST /api/logs HTTP/1.1 X-Signature: a1b2c3d4... Content-Type: application/json { ... }
Queue Transport
The bundle adds a SignatureStamp to the Messenger envelope containing the signature of the serialized AuditLogMessage.
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Message\Stamp\SignatureStamp; // In your message handler $signature = $envelope->last(SignatureStamp::class)?->signature;
Integrations
EasyAdmin Integration
Add the AuditLogCrudController to your DashboardController:
use Rcsofttech\AuditTrailBundle\Controller\Admin\AuditLogCrudController; yield MenuItem::linkToCrud('Audit Logs', 'fas fa-history', AuditLog::class) ->setController(AuditLogCrudController::class);
Benchmarks
| Operation | Time (mode) | Memory (peak) |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Creation (Overhead) | 1.66ms / flush | 11.25 MB |
| Baseline (Auditing Disabled) | 0.68ms / flush | 10.41 MB |
| Audit Retrieval (10 logs) | 5.60ms | 12.86 MB |
| Audit Purge (1000 logs) | 44.14ms | 21.79 MB |
Requirements
- PHP 8.4+
- Symfony 7.4+
- Doctrine ORM 3.0+
License
MIT License.
统计信息
- 总下载量: 8
- 月度下载量: 0
- 日度下载量: 0
- 收藏数: 39
- 点击次数: 2
- 依赖项目数: 0
- 推荐数: 0
其他信息
- 授权协议: MIT
- 更新时间: 2025-12-22